Episode 7 : The Scope Chain, Scope & Lexical Environment
Scope in Javascript is directly related to Lexical Environment.
Let's observe the below examples:
// CASE 1
function a() {
console.log(b); // 10
// Instead of printing undefined it prints 10, So somehow this a function could access the variable b outside the function scope.
}
var b = 10;
a();
// CASE 2
function a() {
c();
function c() {
console.log(b); // 10
}
}
var b = 10;
a();
// CASE 3
function a() {
c();
function c() {
var b = 100;
console.log(b); // 100
}
}
var b = 10;
a();
// CASE 4
function a() {
var b = 10;
c();
function c() {
console.log(b); // 10
}
}
a();
console.log(b); // Error, Not Defined
- Let's try to understand the output in each of the cases above.
- In case 1: function a is able to access variable b from Global scope.
- In case 2: 10 is printed. It means that within nested function too, the global scope variable can be accessed.
- In case 3: 100 is printed meaning local variable of the same name took precedence over a global variable.
- In case 4: A function can access a global variable, but the global execution context can't access any local variable.
To summarize the above points in terms of execution context:
call_stack = [GEC, a(), c()]
Now lets also assign the memory sections of each execution context in call_stack.
c() = [[lexical environment pointer pointing to a()]]
a() = [b:10, c:{}, [lexical environment pointer pointing to GEC]]
GEC = [a:{},[lexical_environment pointer pointing to null]]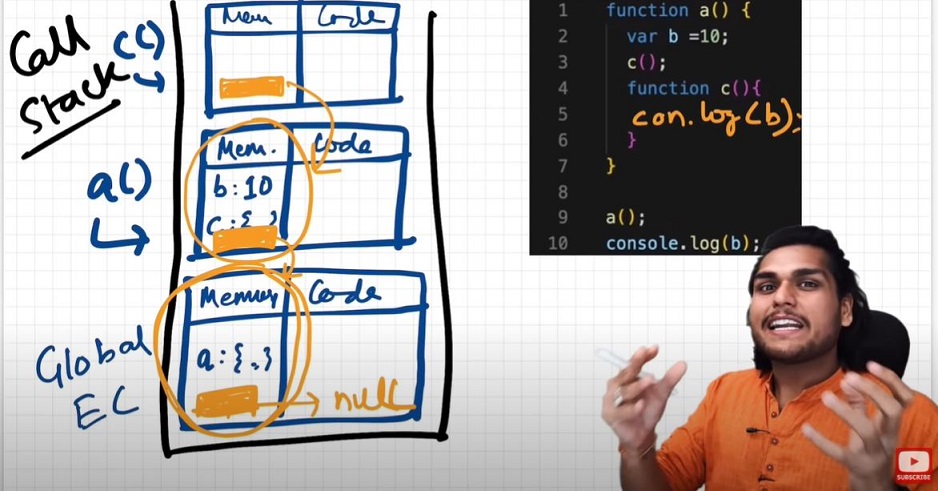
So, Lexical Environment = local memory + lexical env of its parent. Hence, Lexical Environement is the local memory along with the lexical environment of its parent
Lexical: In hierarchy, In order
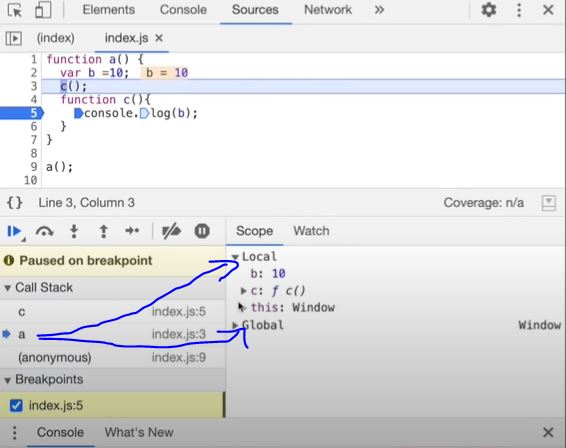
Whenever an Execution Context is created, a Lexical environment(LE) is also created and is referenced in the local Execution Context(in memory space).
The process of going one by one to parent and checking for values is called scope chain or Lexcial environment chain.
function a() {
function c() {
// logic here
}
c(); // c is lexically inside a
} // a is lexically inside global executionLexical or Static scope refers to the accessibility of variables, functions and object based on physical location in source code.
Global {
Outer {
Inner
}
}
// Inner is surrounded by lexical scope of OuterTLDR; An inner function can access variables which are in outer functions even if inner function is nested deep. In any other case, a function can't access variables not in its scope.
Watch Live On Youtube below:
