Episode 2: How JavaScript Code is executed?
Execution Context and Phases
- JavaScript code is executed in execution contexts.
- Execution contexts have two phases: memory creation and code execution.
Memory Creation Phase
- In the memory creation phase, memory is allocated to variables and functions.
- Variables are assigned the value of
undefined. - Functions are stored in memory as they are.
Code Execution Phase
- In the code execution phase, the code is executed line by line.
- Variables created in Memory Creation Phase start assigning value as code executed.
- Functions are invoked by creating a new execution context (Global Execution Context).
- The execution context has its own memory and code components.
- Code inside the function is executed.
returnstatements return control to the invoking context.- Return values are stored in memory if stored in variable.
- The execution context is deleted after the function finishes.

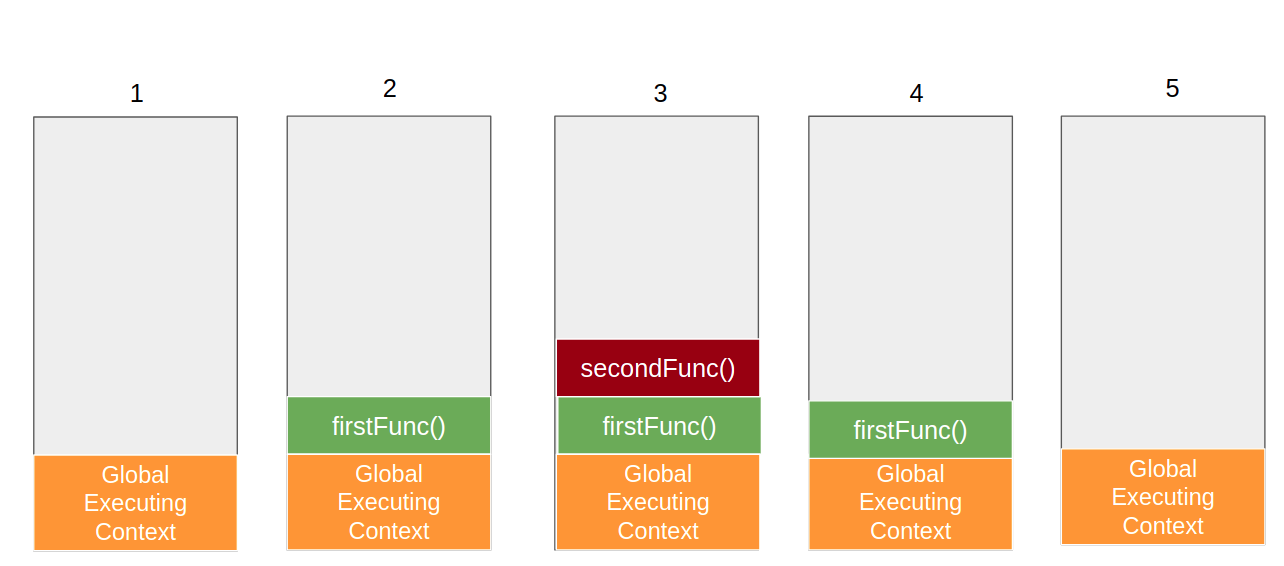
Call Stack
- The call stack manages the execution contexts.
- It maintains the order of execution of execution contexts.
- Each new execution context is pushed onto the stack.
- The topmost execution context is the one currently being executed.
- The bottom execution context is the Global Execution Context and others are Function EC.
- When a function finishes, its execution context is popped from the stack.
- Eventually GEC is also popped from the stack, Execution of program completed.
Watch Live On Youtube below: